Over the last several months the Bee dev team has been hard at work with the rollout of the storage incentives system which will ensure that node operators who share their disk space with the network will get rewarded. Along the way the dev team has been continually testing various aspects of the health of the network and monitoring community feedback in order to diagnose any issues. One issue which has come up is that of node performance. Some node operators may be missing out on earning storage incentives due to insufficient hardware performance. To address this issue, we’ve put together this guide for benchmarking node performance so node operators can make sure that their nodes are running optimally.
Recommended Bee Node Hardware Specifications
Due to a wide variety of variables affecting node performance including different processor architectures, manufacturers, operating systems, network environments, and much more, any hardware recommendations are just a rough guide, and it is important to perform benchmarking tests to find out if your node specifications are sufficient.
Recommended specs for each Bee node:
- Recent generation 2ghz with 2 cores
- 8gb RAM
- 30gb SSD (HDD strongly discouraged)
- 10mbps upload / download speed
Performance Benchmarking Step by Step:
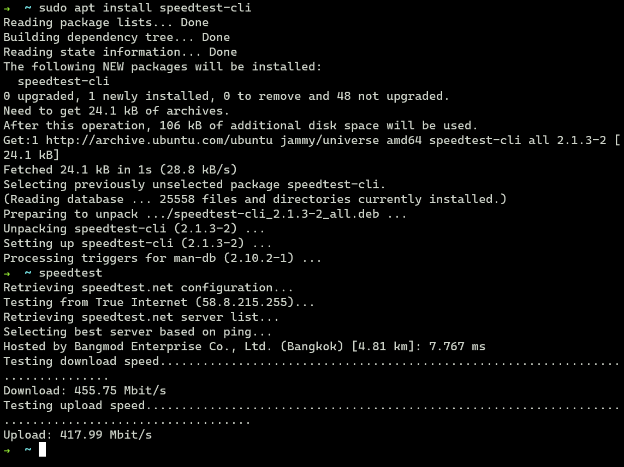
First check that your network download and upload speeds are above 10mbps
sudo apt install speedtest-cli
speedtest
Next check whether hardware performance is sufficient. The sampler process is the main performance affected process for Bee nodes. It is the process where the node takes a sample of data from its reserve and calculates a hash as a part of the storage fee redistribution process. The process may fail or time out if the node’s hardware specifications aren’t high enough. If a node is able to complete the sampler process in under 6 minutes, then its performance should be sufficient. To check a node’s performance the /rchash/{depth}/{anchor} endpoint of the API may be used.
Before proceeding, first check that the node is fully synced, is not frozen, and has sufficient funds to participate in staking. To check node sync status, call the redistributionstate endpoint:
curl -X GET http://localhost:1635/redistributionstate | jq
Response:
{
"minimumFunds": "18750000000000000",
"hasSufficientFunds": true,
"isFrozen": false,
"isFullySynced": true,
"phase": "commit",
"round": 176319,
"lastWonRound": 176024,
"lastPlayedRound": 176182,
"lastFrozenRound": 0,
"block": 26800488,
"reward": "10479124611072000",
"fees": "30166618102500000"
}
Confirm that hasSufficientFunds is true, and isFullySynced is true before moving to the next step. If hasSufficientFunds if false, make sure to add at least the amount of xDAI shown in minimumFunds (unit of 1e-18 xDAI). If the node was recently installed and isFullySynced is false, wait for the node to fully sync before continuing. After confirming the node’s status, continue to the next step.
The {anchor} value can be set to any random string. To get the {depth} value, first call the topology debug API endpoint using jq to filter for the depth `value:
sudo curl -sX GET http://localhost:1635/topology | jq '.depth'
Output:
8
Call the endpoint using the value returned (8 in our example) like so:
sudo curl -X GET http://localhost:1633/rchash/8/randomstring | jq
If the sampler runs successfully, you should see output like this:
% Total % Received % Xferd Average Speed Time Time Time Current
Dload Upload Total Spent Left Speed
100 659 100 659 0 0 3 0 0:03:39 0:02:54 0:00:45 161
{
"Sample": {
"Items": [
"000003dac2b2f75842e410474dfa4c1e6e0b9970d81b57b33564c5620667ba96",
"00000baace30916f7445dbcc44d9b55cb699925acfbe157e4498c63bde834f40",
"0000126f48fb1e99e471efc683565e4b245703c922b9956f89cbe09e1238e983",
"000012db04a281b7cc0e6436a49bdc5b06ff85396fcb327330ca307e409d2a04",
"000014f365b1a381dda85bbeabdd3040fb1395ca9e222e72a597f4cc76ecf6c2",
"00001869a9216b3da6814a877fdbc31f156fc2e983b52bc68ffc6d3f3cc79af0",
"0000198c0456230b555d5261091cf9206e75b4ad738495a60640b425ecdf408f",
"00001a523bd1b688472c6ea5a3c87c697db64d54744829372ac808de8ec1d427"
],
"Hash": "7f7d93c6235855fedc34e32c6b67253e27910ca4e3b8f2d942efcd758a6d8829"
},
"Time": "2m54.087909745s"
}
If the Time value is higher than 6 minutes, then the hardware specifications for the node may need to be upgraded.
If there is an evictions related error such as the one below, try running the call to the /rchash/{depth}/{anchor} endpoint again:
error: "level"="error" "logger"="node/storageincentives"
"msg"="make sample" "error"="sampler: failed creating sample:
sampler stopped due to ongoing evictions"
While evictions are a normal part of Bee’s standard operation, the event of an eviction will interrupt the sampler process.
If you are still experiencing problems, you can find more help in the node-operators Discord channel (for your safety, do not accept advice from anyone sending a private message on Discord).
Discussions about Swarm can be found on Reddit.
All tech support and other channels have moved to Discord!
Please feel free to reach out via info@ethswarm.org
Join the newsletter! .