Bee 2.2.0 Node Operator’s Upgrade Guide
This node operator’s guide contains step by step instructions for the requirements to upgrade your node to 2.2.0 as well as instructions for other new features such as neighborhood hopping and partial withdrawals. To learn more about all the new features included in the 2.2.0 release, check out the one week announcement article.
Required 2.2.0 Upgrade Steps
The basic upgrade process is as follows:
Step One: Unstake while on 2.1.0
Step Two: Stop your node
Step Three: Update to 2.2.0 & Restart Node
Step Four: Restake xBZZ
Step One: Unstake while on 2.1.0
Once the full version of 2.2.0 is released on Github, the current staking contract will be disabled, and withdrawals will be enabled. After the release of 2.2.0 on Github you should unstake your xBZZ BEFORE upgrading from 2.1.0 to 2.2.0.
Once the contract is disabled, withdraw all your stake by calling the /stake endpoint with the DELETE method (there is no time limit for moving your stake, however the longer you wait, the more potential rewards are lost):
curl -X DELETE http://localhost:1633/stake
This command will withdraw all stake from your node to your node’s Gnosis Chain address.
Step Two: Stop your node
Stop your node. This step will vary depending on your setup, but will likely look something like one of these commands depending on your install method:
sudo systemctl stop bee
or
docker compose down
or
docker stop <container_name_or_id>
While your node is stopped, remove these three options from your node’s configuration as they are no longer supported:
# bcrypt hash of the admin password to get the security token
admin-password: ""
# debug HTTP API listen address
debug-api-addr: :1635
# enable debug HTTP API
debug-api-enable: false
Read more about this and also other required steps for securing your node in the “Removal of the Bee Debug API” section further below in this article.
Step Three: Update to 2.2.0 & Restart Node
In this step, upgrade your node to 2.2.0 using your preferred installation method, and restart your node.
The specific restart command will depend on your installation method (Docker, install script, package installer, etc.) If you are unsure, check with the node operator’s Discord group.
Before every Bee client upgrade, it is best practice to ALWAYS take a full backup of your node.
The 2.2.0 upgrade includes a localstore migration which will take an extended time to complete (the exact time will vary based on your particular system specs). You can check your node’s logs for messages related to the migration in order to check on the migration progress.
Turning off your node before the migration is complete could cause your node to become corrupted! ⚠️
Step Four: Restake xBZZ
After upgrading to 2.2.0 and restarting your node, restake your xBZZ. In order to stake the minimum required 10 xBZZ you can use the following command:
curl -X POST localhost:1633/stake/100000000000000000
Your upgrade to 2.2.0 is now complete. From here on, your node will continue to participate in the redistribution game as normal.
Neighborhood Hopping (Optional)
Following the 2.2.0 update, you now have the option to set your node to operate in any neighborhood of your choice. You can use the option target-neighborhood in order to switch your node over to a new neighborhood. There is no requirement to use this option, your node will simply continue to operate in its current neighborhood following the 2.2.0 upgrade.
Checking if in Overpopulated Neighborhood
For a quick check of your node’s neighborhood population, we can use the /status endpoint:
curl -s http://localhost:1633/status | jq
{
"peer": "e7b5c1aac67693268fdec98d097a8ccee1aabcf58e26c4512ea888256d0e6dff",
"proximity": 0,
"beeMode": "full",
"reserveSize": 1055543,
"reserveSizeWithinRadius": 1039749,
"pullsyncRate": 42.67013868148148,
"storageRadius": 11,
"connectedPeers": 140,
"neighborhoodSize": 6,
"batchCommitment": 74463051776,
"isReachable": false
}
Here we can see that at the current storage depth/radius of 11, our node is in a neighborhood with size 6 from the neighborhoodSize value. Using the Swarmscan neighborhoods tool we can see there are many neighborhoods with fewer nodes, so it would benefit us to move to less populated neighborhood:
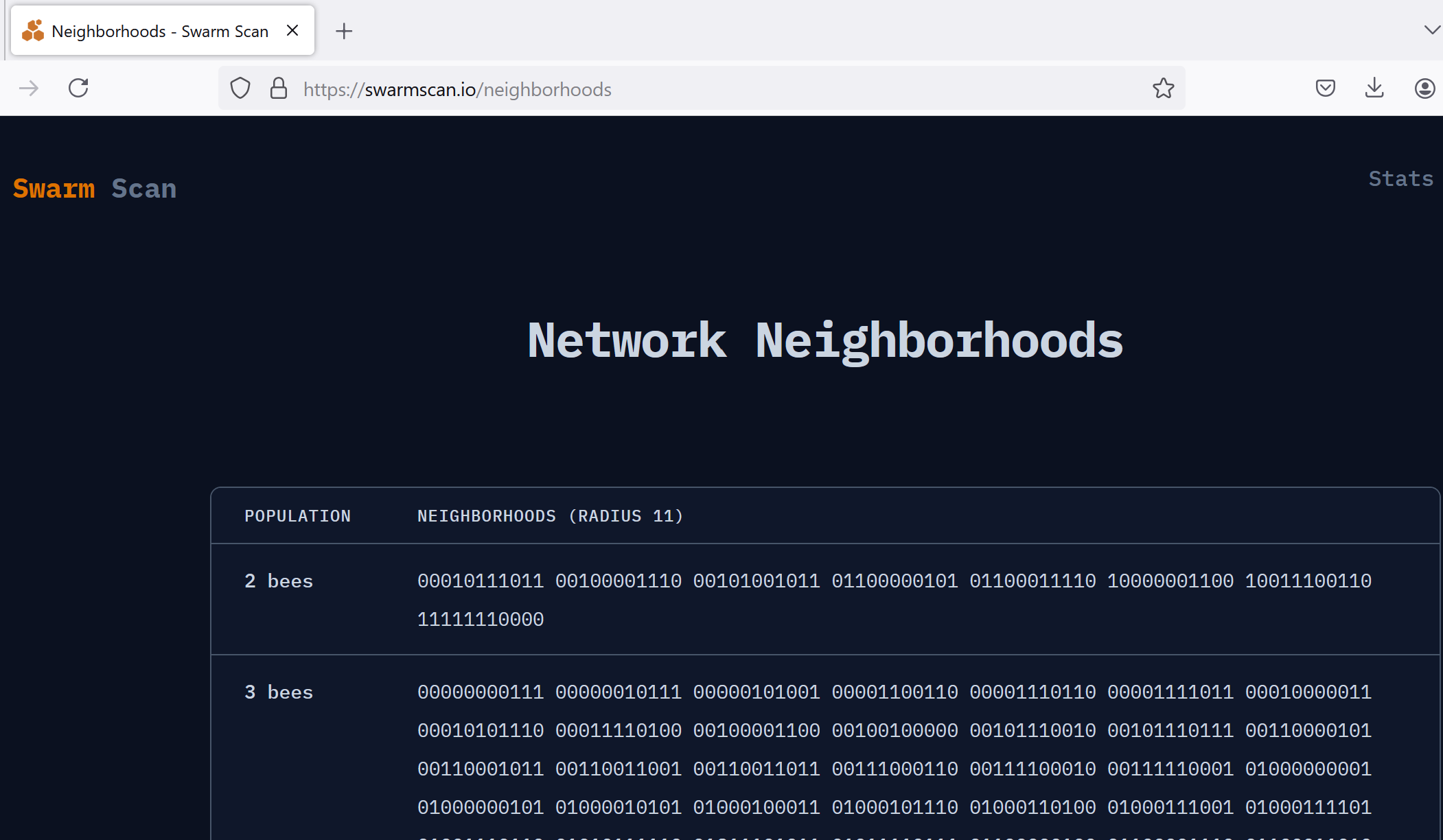
While you might be tempted to simply pick one of these less populated neighborhoods, it is best practice to use the neighborhood suggester API instead, since it will help to prevent too many node operators rapidly moving to the same underpopulated neighborhoods, and also since the suggester takes a look at the next depth down to make sure that even in case of a neighborhood split, your node will end up in the smaller neighborhood.
curl -s https://api.swarmscan.io/v1/network/neighborhoods/suggestion
Copy the binary number returned from the API:
{"neighborhood":"01100011110"}
Use the binary number you just copied and set it as a string value for the target-neighborhood option in your config.
## bee.yaml
target-neighborhood: "01100011110"
target-neighborhood option by updating your bee.yaml file, adding the --target-neighborhood command line flag, or edit a .env file, among several possible common options.
Partial Withdrawals
2.2.0 will support the partial withdrawal of stake based on the price of xBZZ. In cases that the price of xBZZ rises so much that it is more than enough to act as collateral, a partial withdrawal will be allowed down to the minimum required stake (which, as mentioned in the section above, is no longer statically set, but depends dynamically on the price of xBZZ):
Step One:
Check for withdrawable stake:
curl http://localhost:1633/stake/withdrawable | jq
If there is any stake available for withdrawal, the amount will be displayed in PLUR:
{
"withdrawableStake": "18411"
}
Step Two:
Withdraw available stake:
If there is any stake available for withdrawal, you can withdraw it using the DELETE method on /stake/withdrawable:
curl -X DELETE http://localhost:1633/stake/withdrawable
Removal of the Bee Debug API
/auth and /refresh endpoints, Bee client users are now responsible for securing their Bee API endpoint themselves.
While the use of a firewall or other security measures are recommended, one other practical solution is to simply make sure that the Bee API is bound to the localhost only by default in your node’s configuration options. This is now the new default configuration for new nodes, but you must update it manually for any already existing nodes as simply upgrading to 2.2.0 will not modify your configuration options. Make sure to append the localhost address of 127.0.0.1 to each api-addr: port (:1633 by default).
# HTTP API listen address
api-addr: 127.0.0.1:1633
Make sure that for your p2p-addr: option you DO NOT modify it to limit it to localhost, as it must be publicly available in order to communicate with the network.
# P2P listen address
p2p-addr: :1634
You must also remove these three related options from your configuration which are no longer supported:
# bcrypt hash of the admin password to get the security token
admin-password: ""
# debug HTTP API listen address
debug-api-addr: :1635
# enable debug HTTP API
debug-api-enable: false
# enable permission check on the http APIs
restricted
Wrapping Up
It’s crucial for you to follow the instructions in this guide to maintain your node’s eligibility for rewards and ensuring optimal performance. We also encourage you to take advantage of the new features such as ACT, neighborhood hopping (and the new staking strategies it enables), and partial withdrawals. To find out more general information about the 2.2 release, check out the one week notice article.
Discussions about Swarm can be found on Reddit.
All tech support and other channels have moved to Discord!
Please feel free to reach out via info@ethswarm.org
Join the newsletter! .




